FLOWCHEM® – Oxygen binders for boiler feed water treatment

The task
Oxygen, carbon dioxide and nitrogen are removed from additional or top-up water as well as returned condensate, without thermal degassing (usually temperatures between > 85°C and > 95°C, i.e. oxygen levels between around 2.2 mg/L and 0.86 mg/L) or with thermal pressure degassing (temperatures between > 100°C and 110°C, i.e. oxygen level of < 0.02 mg/L and < 1mg/L carbon dioxide). This water is referred to as boiler feed water and it comes very close to the standards of the VdTÜV (Association of Technical Inspection Agencies), VGB, TRD 611 (Technical Rules for Steam Boilers) and DIN (German Industry Norms) for the prevention of pitting and surface corrosion in boiler areas with water contact.
The challenge
- Binding the (residual) oxygen
- Preventing pitting and surface corrosion
- Passivation of the metal surface
- No tendency towards foam formation
The solution
- Using suitable FLOWCHEM® products for softened, partially or fully demineralised feed water.
- Suitability for applications in the food sector
- Not a hazardous substance according to TRG 608 (Technical Rules for Hazardous Substances)
- Simple and safe handling of FLOWCHEM® products
Benefits for our customers
- Reduced costs for energy and water treatment
- High degree of operational safety and availability of boiler systems
- Compliance with legal requirements
FLOWCHEM® – Hardness stabilisers and corrosion protection for steam production
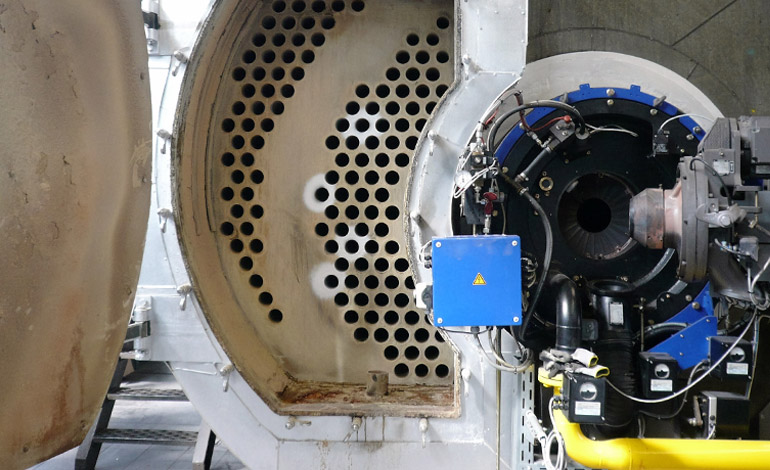
The task
The Technical Rules for Steam Boilers (TRD) have been issued to provide rules for technology according to the Steam Boiler Code. The TRD supply users with general instructions for boiler operation. Steam and hot water generators may only be used with "appropriately treated feed water", according to the rules TRD 611, TRD 612, information sheets by VdTÜV (Association of Technical Inspection Agencies)/the energy efficiency association AGFW (TCh 1466/FW 510), guidelines by the technical inspection association TÜV and the VGB, DIN EN 12953-10:2003, DIN EN 12952-12:2003 and DIN EN 285. This refers to water that allows for corrosion and coating free boiler operations and that complies with mandatory requirements.
The challenge
- Corrosion and coating-free operation for the entire boiler system
- Prevention of foam formation of the boiler water
- Reduced desludging / desalination of the boiler water
- High degree of steam purity
The solution
- Using suitable FLOWCHEM® products for various technical and hygienic operating requirements
- High degree of substance accumulation in the boiler water
- Formation of a homogeneous protective magnetite layer
- Simple and safe handling of FLOWCHEM® products
Benefits for our customers
- Cost savings for top-up and waste water
- Optimisation of energy and fuel costs
- Improved boiler efficiency
- High degree of operational safety and availability of boiler systems
- Compliance with legal requirements
FLOWCHEM® – Alkalinising agents for steam and condensate treatment

The task
For boiler feed water, which is usually a mixture of additional water and condensate, to meet requirements, the condensate must also be of appropriate quality.
The risk of corrosion caused by oxygen and carbon dioxide is particularly high, where steam is used through a number of condensation stages in different parts of the plant. This is why it is wise to perform steam / condensate treatment.
The challenge
- Even product distribution at the condensate / steam stage
- Preventing pitting and surface corrosion
- Steam purity
- Increasing cost effectiveness of the production process
The solution
- Using suitable FLOWCHEM® products where direct or indirect steam is used in production
- Low application concentrations
- Increasing the service life of downstream parts of the plant
Benefits for our customers
- No production downtime
- Reduction of repair and maintenance costs
- Reduced use of expensively treated additional or top-up water
- Reduction of treatment and waste water costs
FLOWCHEM®– Products for district heating and hot water recirculation systems

The task
Hot water recirculation systems are used increasingly to supply heat to building complexes, industrial and municipal users. Heating takes place either directly via combustion plants or indirectly via heat exchangers.
The requirements for filling and top-up water for these plants are compiled in the guidelines issued by the German Technical Inspection Association TÜV and the Association of German Engineers VDI.
Hygienic and toxicological aspects are important, in addition to fundamental principles of water chemistry.
We generally distinguish between a saline and a low-salt operating mode for circulating water.
The challenge
- Preventing the formation of coating in the case of direct heating
- Preventing corrosion in systems featuring an extensive network
- Specialised products for drinking water systems
- Preventing accumulation and an increase of conductivity
The solution
- Using suitable FLOWCHEM® products for softened, partially or fully demineralised filling and top-up water.
- Suitability for applications in the food sector
- Clearance certificates for conditioning agents
- Simple and safe handling of FLOWCHEM® products
Benefits for our customers
- Reduced costs for energy and water treatment
- High degree of operational safety and availability of boiler systems
- Compliance with legal requirements